Three Key Points of Wireless Charging Technology
As technology advances and the demand for convenience increases, wireless charging technology has become a hot topic in the field of electronic devices. From smartphones to electric vehicles, the application scope of wireless charging is expanding. However, achieving efficient, safe, and stable wireless charging requires solving many technical challenges. This article will discuss the three key points of wireless charging technology: energy transfer efficiency, compatibility, and safety.
Energy Transfer Efficiency
Energy transfer efficiency is a core issue in wireless charging technology. The basic principle of wireless charging is to transmit electrical energy from the transmitter to the receiver through an electromagnetic field. The efficiency of this process directly affects the charging speed and the user experience.
1. Electromagnetic Coupling Method
Wireless charging mainly relies on electromagnetic coupling methods, with magnetic induction and magnetic resonance being the most common techniques. Magnetic induction is suitable for short-distance transmission, with high efficiency but limited transmission distance. Magnetic resonance can achieve medium-distance transmission, with slightly lower efficiency but a broader transmission range. Therefore, selecting the appropriate electromagnetic coupling method according to the application scenario is key to improving energy transfer efficiency.
2. Resonance Frequency Matching
In magnetic resonance technology, resonance frequency matching is crucial. The energy transfer efficiency reaches its peak only when the resonance frequencies of the transmitter and receiver are precisely aligned. Thus, designing high-precision resonance frequency adjustment circuits and algorithms is significant for enhancing wireless charging efficiency.
3. Coil Design
The design of the coils in both the transmitter and receiver also directly impacts energy transfer efficiency. Optimizing the shape, size, and material of the coils can minimize energy loss. In high-power wireless charging applications, the cooling and heat dissipation design of the coils is also a critical issue that cannot be overlooked.
Compatibility
The widespread application of wireless charging requires solving compatibility issues between different devices. With the diversification of wireless charging standards and the increase in application scenarios, compatibility problems have become more prominent.
1. Standardization
Currently, there are multiple wireless charging standards on the market, such as Qi, PMA, and AirFuel. To achieve compatibility between different devices, international standard organizations and industry alliances are working to promote the development and adoption of unified standards. Adopting a unified wireless charging standard can effectively reduce device incompatibility issues and promote the popularization of wireless charging technology.

2. Multi-Mode Charging
To meet different charging needs, designing multi-mode wireless chargers has become a trend. These chargers can automatically recognize and adapt to different charging standards and power requirements, providing efficient charging solutions for various devices.
3. Intelligent Recognition Technology
Intelligent recognition technology can help wireless chargers automatically detect and adapt to different devices and charging needs. For example, by integrating NFC (Near Field Communication) technology, chargers can quickly identify device types and adjust charging parameters accordingly, achieving higher compatibility and better user experience.

Safety
Safety is another crucial factor to consider in the application of wireless charging technology. Efficient and safe wireless charging requires not only preventing overheating and overload but also avoiding electromagnetic radiation interference with humans and other electronic devices.
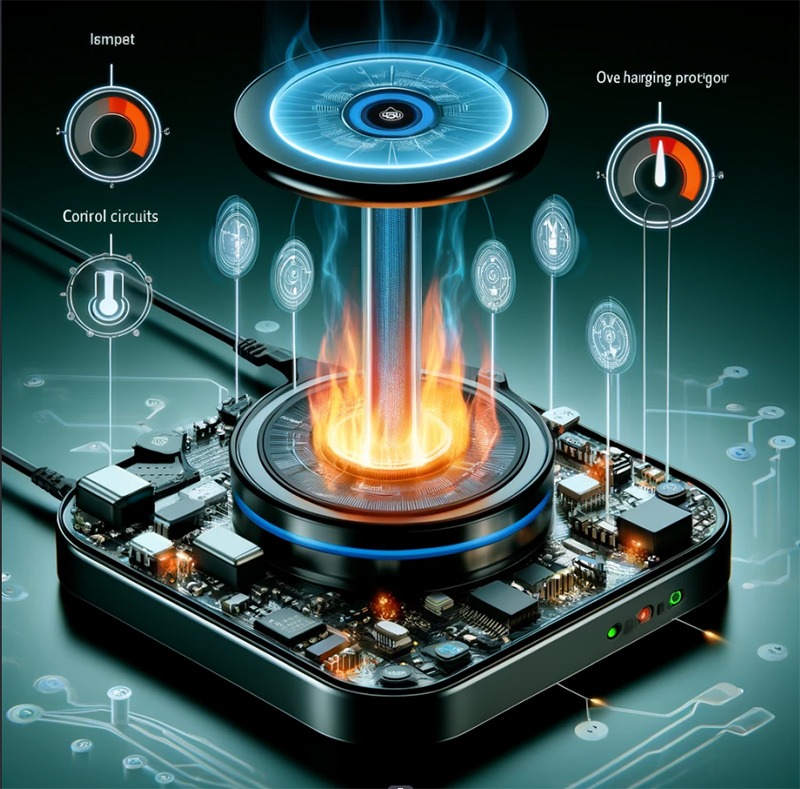
1. Overheat Protection
The energy transfer and conversion process in wireless charging inevitably generate heat. To prevent devices from overheating, effective overheat protection mechanisms must be designed. For example, integrating temperature sensors and control circuits in both the transmitter and receiver can monitor the temperature in real-time and adjust the charging power or stop charging when necessary.

2. Electromagnetic Shielding
The electromagnetic field during wireless charging may interfere with surrounding electronic devices. Therefore, designing effective electromagnetic shielding measures, such as using shielding materials or designing reasonable electromagnetic field distribution, can effectively reduce electromagnetic interference and ensure the normal operation of other devices.
3. Safety Protocols
Designing safe and reliable wireless charging protocols is crucial to protect users and devices. These protocols should prevent overload and short circuits and address data security issues. For instance, using encrypted communication and authentication technology can prevent unauthorized use of wireless chargers and protect users’ data and device security.
The development of wireless charging technology has brought great convenience to the use of electronic devices, but achieving efficient, compatible, and safe charging still faces many challenges. By optimizing energy transfer efficiency, improving device compatibility, and ensuring charging safety, we can further promote the popularization and application of wireless charging technology. With continuous technological advancement and gradual standardization, wireless charging is expected to become the mainstream charging method in the future, bringing more convenience and innovation to people’s lives and work.
